|
|


The Lorenz Attractor
The Lorenz Attractor, which is the solution to Lorenzs differential equations for modeling the atmosphere, is an example of this. The state of the system orbits around one lobe, jumps to the other, and so on, in a chaotic manner.
Hyperion: The Rebel Satellite
There are some examples of chaotic motion in the solar system but by far the most striking case is that of Hyperion, the fourth satellite of Saturn. Hyperion, which was first observed in 1848, is one of the most irregularly shaped Hyperion, which was first observed in 1848, is one of the most irregularly shaped objects in the solar system and it is this
|
|
irregularity that gives rise to chaotic dynamics. Even though Hyperion moves in a regular elliptic orbit, its rate of rotation and the direction of its axis vary chaotically. This gives rise to a tumbling motion which renders its orientation in space unpredictable.
|
|
The reason for this behaviour is its highly irregular shape. The gravitational field of Saturn tends to pull the part of Hyperion closer to it more strongly than the part that faces away from it, resulting in a tidal torque.
|
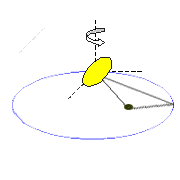
Orbit of Hyperion
|
The differential equations that describe the resulting motion have chaotic solutions. The complex tumbling motion of Hyperion can be simplified by considering only the variation in the rate of rotation about its axis, neglecting the change in the direction of this axis, by assuming it to be fixed normal to the orbital plane. (This is justified because the tidal torques tend to bring Hyperion into this orientation.)
Copyright © 2022 ICICI Centre for Mathematical Sciences
All rights reserved. Send us your suggestions at
|
|